Power and Energy
Electrical power
Normally power is the rate of work done or energy absorbed/delivered per unit time. So, electric power means the time rate of energy transferred (absorbed/delivered) in an electric circuit. S.I unit of power is the watt (W). One watt means transferring of 1-joule energy per second.
\[P= \frac{ \Delta W}{ \Delta t} \]
- Where P=average power.
- ΔW=work done or energy transferred in time t.
- Δt=total time.
Instantaneous power
If power changes with respect to time then we have to calculate power at an instant of time, which is called instantaneous power.
\[p=p(t)= \lim_{ \Delta t \rightarrow 0} \frac{ \Delta W}{ \Delta t} \Rightarrow p= \frac{dw}{dt} \]
Relation between power, voltage, and current
\[ p= \frac{dw}{dt} = \frac{dw}{dq} \times \frac{dq}{dt} =vi\]
The power absorbed or delivered by an electrical element is given by product of voltage across that element and current through it.
How to determine the sign of power? (Passive Sign Convention )
If power is positive: Absorbing power.
if power is negative: Delivering power.
But the question is how do we know that power is positive or negative.
To determine this we have to understand passive sign convention. Passive sign convention states that when the current enters through the positive terminal of an element then p=+vi. But if the current enters through the negative terminal then p=-vi.
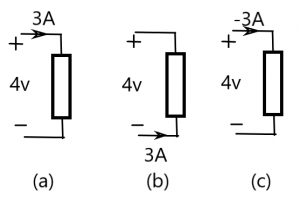
- In figure number (a), current 3A enters from the positive terminal. Therefore p=+vi=+(4)(3)=+12W .That means in figure (a) element is absorbing 12W power.
- In figure number (b), current 3A enters from the negative terminal. Therefore p=-vi=+(4)(3)=-12W .That means in figure (b) element is delivering 12W power.
- In figure number (c), current -3A enters from the positive terminal. Therefore p=+vi=+(4)(-3)=+(-12W) .That means in figure (c) element is absorbing -12W power.
Conceptual understanding of power absorbed and power delivered
As we can see from the above figure, figure number (b) and (c) are equivalent, this implies that
12W delivered= -12W absorbed
⇒Power delivered=-Power absorbed
◊♦We can write power delivered by elements in terms of power absorbed by changing its sign or vice-versa.
◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦◊♦
The algebraic sum of power in a circuit at any instant of time must be zero due to the law of conservation of energy.
∑p=0
Note: In this equation either take all elements as power absorbing or take all elements as the power delivering not both.
For Example:
Let E1, E2, E3, E4, E5 are five elements in a circuit. Where E1 and E4 are power absorbing elements that are absorbing power P1 and P4 respectively.While E2, E3, E5 are power delivering elements that are delivering power P2, P3, P5 respectively.
- E1= P1 (absorbing)= -P1 (delivering)
- E2= -P2 (absorbing)= P2 (delivering)
- E3= -P3 (absorbing)= P3 (delivering)
- E4= P4 (absorbing)= -P4 (delivering)
- E5= -P5 (absorbing)= P5 (delivering)
All above five equation comes from this equation: Power delivered=-Power absorbed
Now if we take total power in absorbing, then
⇒P1 -P2– P3+P4 – P5=0
⇒P1 +P4 =P2+P3 +P5
⇒Total power absorbed in a circuit=Total power delivered.
Similarly, we can take total power by taking all elements as delivering power. We get the same results.
Electrical Energy
Energy is the capacity of doing work .S.I unit of energy is joule(J).
Law of conservation of energy: Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed, it can only be transferred from one form of energy to another form. Electrical energy is transferred from one element to another element in a circuit by the flow of charge.
The energy absorbed or supplied by an element from time t0 to time t is:
\[E=W= \int_{t0}^t p(t)dt= \int_{t0}^t vidt \]
♦Electric power utility companies measure energy in watt-hours or Kilo-watt-hours.
1Wh=3600 joule
1KWh= 36×105